How to Charge AirPods Without a Case
Discover the truth about how to charge AirPods without a case. Uncover myths, find alternatives, and safeguard your audio experience.
A driver unit is a component responsible for the reproduction of sound in a headphone. Depending on the type of headphone driver, sound can vary with some drivers giving out the best sound. Because all headphone drivers use different materials and techniques to reproduce sound, each comes with its advantages and disadvantages.
In total, six headphone drivers currently exist in the market. Today, I will talk about these various driver technologies and what you can expect from them.
A typical driver unit consists of a magnet, voice coils, and a diaphragm.
Below are the five different types of headphone drivers:
Balanced armature drivers (BA drivers) have been around for a very long time. Older balanced armature drivers were much larger and even different than today’s BA drivers.
Balanced armature drivers are the smallest and commonly found in IEMs, but not all IEMs have BA drivers.
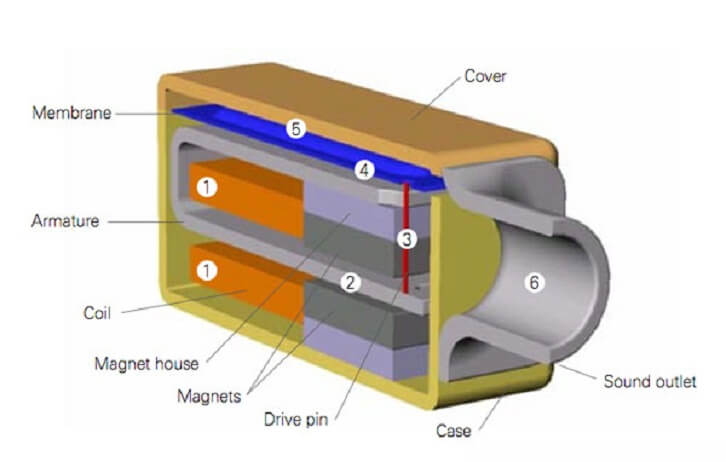
Balanced Armature Illustration | InnerFidelity
First, the incoming audio signal moves through the coil (1) that wraps the armature. Due to the magnetic flux induced in the armature (2), the end of the armature is drawn towards one of the poles of the magnets. As the electrical signal goes up and down, the armature to follows and goes up and down. A driver pin (3) located at the end of the armature transfers even the small movements to the diaphragm (4). As the diaphragm moves, it changes the volume of air enclosed above it (5), and this produces the sound that escapes out of the front nozzle (6).
Due to their small size and high efficiency, balanced armature drivers are suitable for in-ear monitors. Because of this most balanced armature headphones will have between 1- 4 drivers while custom-made drivers will have as many as 15 armatures. However, the technology behind balanced armature driver is still expensive.
To produce sound, unlike Dynamic drivers, balanced armature drivers will not displace air. This, in turn, leads to a lack of superior bass response.
To address this, manufacturers will add dynamic drivers to make up for the lack of bass response. This creates a different driver known as the hybrid driver.
Because they do not displace air to give out sound, balanced armature drivers will lack additional air vents. This helps in offering better isolation to outside noises.
These drivers are the most common drivers in headphones and also come at relatively low prices. Dynamic drivers exist in different sizes ranging from the small drivers in IEMs to the large ones in home speakers.
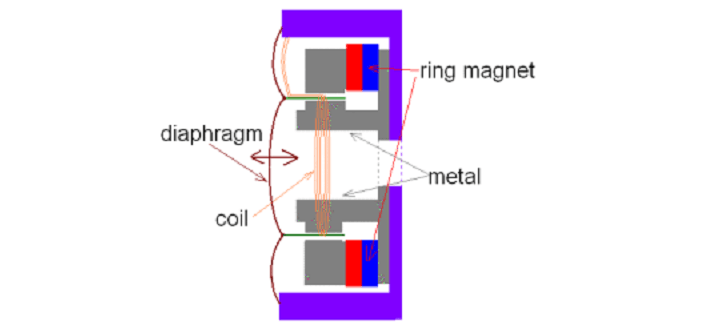
Dynamic driver illustration | DiyAudioHeaven
In dynamic drivers, when you introduce current, the voice coil moves, and because it is held together with the diaphragm, they move together causing sound reproduction. This working principle is why dynamic drivers are also referred to as “moving coil drivers.”

50mm dynamic headphone drivers
Unlike balanced armature drivers, dynamic drivers are often vented and move air by design. Due to this dynamic drivers will offer better reproduction of the bass frequencies as compared to BA drivers.
The excellent bass response reproduction makes dynamic headphones a preferred option by bassists, drummers (see also the best headphones for drumming here) or bass heads in the audiophile world.
Also referred to as isodynamic, magneplanar or orthodynamic drivers, planar magnetic drivers typically consist of two main components; magnets and a diaphragm with a circuit. Due to their unique design and functionality, planar magnetic drivers will overcome many limitations that come with dynamic drivers.
Like dynamic drivers, planar magnetic drivers use magnetic fields to produce sounds.
However, with planar magnetic drivers, the diaphragm is not attached to any coil, but instead, a coil stretches and goes through the diaphragm. Also unlike the dynamic drivers, a planar magnetic driver’s diaphragm is sandwiched between two magnets.
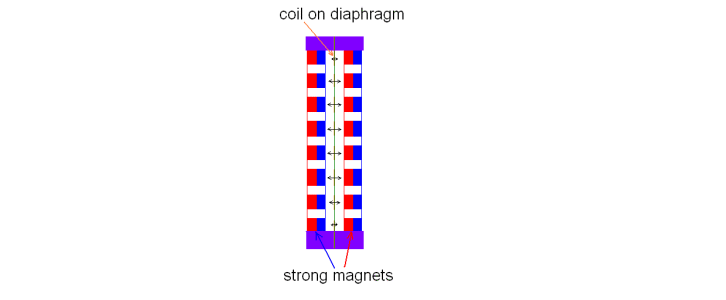
A typical planar magnetic driver illustration | DiyAudioHeaven
When current is applied, it flows through the wire and interacts with the magnetic fields in the diaphragm creating an electromagnetic force that moves the diaphragm back and forward creating sound.
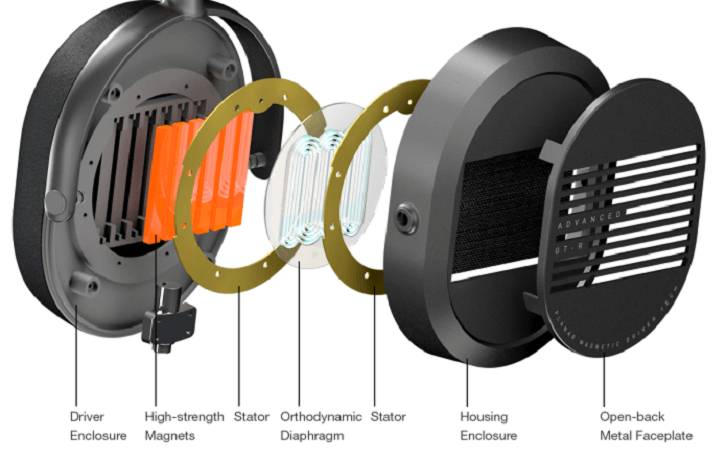
GT-R Planar Magnetic Headphones driver
The word “planar” in planar magnetic drivers, refer to the magnetic field that is distributed in the same plane parallel to the diaphragm. Unlike dynamic drivers, the diaphragm of a planar magnet driver is much thinner and very lightweight.
Because the diaphragm of an orthodynamic driver has to vibrate evenly, strong magnets are provided. The efficiency of a planar magnetic driver will depend on the strength of the magnets, the distance between the membrane, the number of windings in the coil, as well as the current supplied.
This is the most expensive of the headphone driver technologies.
Electrostatic drivers are rare, due to their high prices and require special amplification called energizers to work properly. However, they are the best when it comes to the reproduction of sound.
Their design is made to create a near-flawless sound detail.
Electrostatic drivers work on the principle of static electricity.
When an electrical sound signal passes through the electrodes, it creates an electrical field. This causes the diaphragm/membrane which is sandwiched between the two electrodes to be attracted to one of the electrode.
When the diaphragm moves, there is displacement of air through the perforations. This mechanism together with a continuously changing electrical signal results in generation of sound.
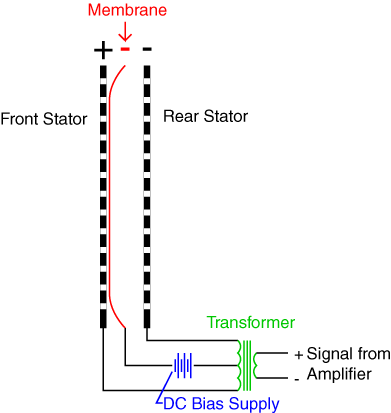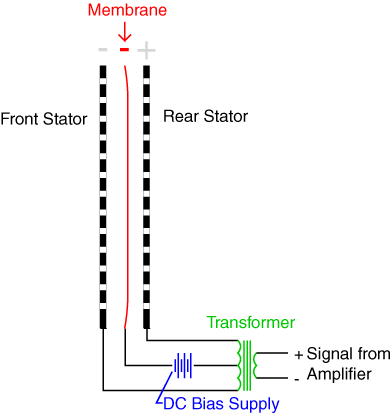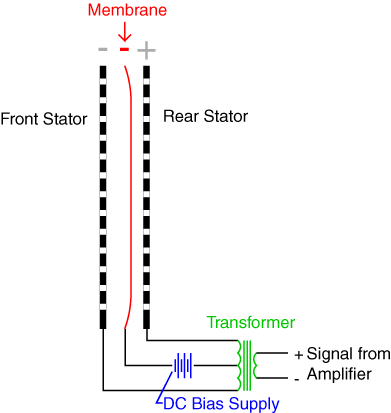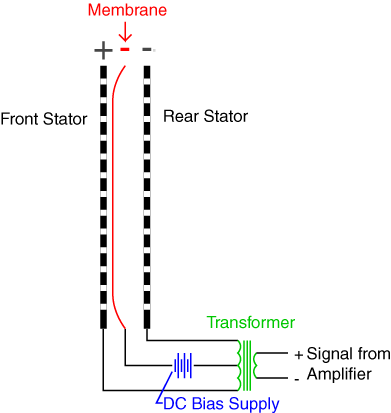
Electrostatic drivers working principle
Electrostatic drivers lack the moving metal components. Because of this, they end up reproducing a virtually distortion-free sound. While this type of accuracy and sound reproduction is sought after by most people, the cost of these drivers makes them only sought after by audio enthusiasts.
Bone conduction technology is gaining ground in the headphone world.
Unlike other headphone drivers where sound passes through your ears, bone conduction drivers allow you (and even deaf people) to hear music by vibrating on the bones of your face, which are the jaw bones and temporal bones.
Bone conduction drivers come in two types; mechanical and magnetostriction drivers. Both require pressing against the bones in your face, about an inch in front of your ears to pass the sound using vibrations to your inner ear.
Bone conduction headphones work using vibrations. A bone conduction driver will decode sound waves and convert them into vibrations. When the driver is placed on the bone near your ear, vibrations transfer directly to the middle ear where it enters the cochlea and you can hear the sound.
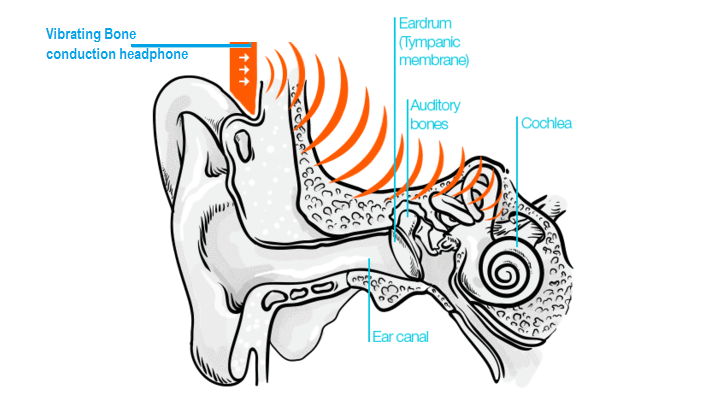
Bone Conduction Headphones working principle
Unlike regular headphones, bone conduction headphones replace the work done by your eardrums.
Due to this, Bone conduction headphones can be useful cases where hearing loss is because of a damaged eardrum. People with hearing difficulties are also able to hear better when using bone conduction headphones.
In the military, the use of bone conduction technology has also been in use to give orders on the battlefield to a soldier without him/her losing focus of the surrounding.
Sportsmen and athletes can also apply this technology to be aware in their surrounding when exercising while still listening to their favorite music.
For a full article about how bone conduction headphones work, check out our full guide.
A hybrid driver pairs a dynamic and balanced armature together.
Hybrid drivers will use two or more drivers to deliver a well-received sound signature. The use of two or more drivers makes sure every sound frequency is well represented giving a vibrant and detailed sound with the warmth and bass that many people seek.
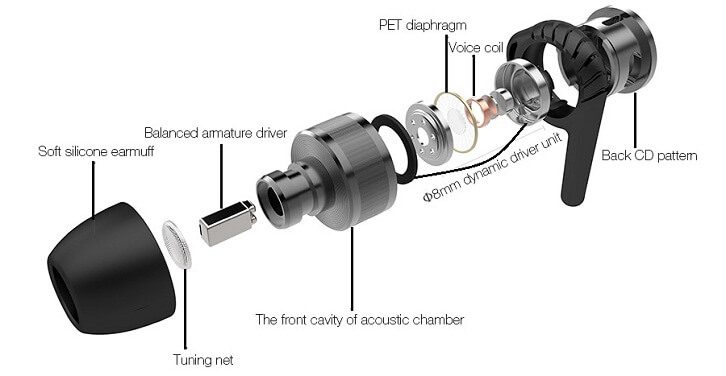
A hybrid in-ear-headphone unit
Sound reproduction between all these drivers is different. However, electrostatic headphones offer the best sound. But, due to their cost, they are not affordable to most people.
However, you can buy, if lucky, a pair of old electrostatic headphones cheaply on eBay but getting one on the high street would be costly.
Planar magnetic headphones come in as a cheaper alternative to electrostatic headphones. Planar magnetic headphones end up giving out a more neutral frequency response which is much balanced. If you wish to know what frequency response is good for headphones, you can read our article about that.
Because of the “planar wave-front”, planar magnetic drivers have a wider soundstage. This is because in planar magnetic drivers, the planar wave-front mechanism eliminates the bouncing of sound thereby creating a better and wider illusion of soundstage.
For a long time, planar magnetic headphones have been associated with bulkiness. While this has been the case, improvements in technology have led to improved and portable planar headphones such as the RHA in-ear planar are slowly gaining ground on the market. The HiFiMAN team also offers cheap planar magnetic headphones that are portable.
Dynamic headphones are the most common and are the best in reproducing low-end (bass) frequencies. Also, Because of their Versatility, Dynamic drivers produce better sound; take for example the Sennheiser HD600.
Most Dynamic headphones can also work without the need for amplification, This makes them ideal for use with portable music players or smartphones.
However, unlike planar magnetic headphones, dynamic headphones are more prone to sound distortion when using them at high volumes.
Balanced armatures are mostly common in portable headphone designs. Though the lack of air vents causes less bass response, this mechanism makes them the best drivers when it comes to noise isolation.
When it comes to sound reproduction, BA headphones are best in reproducing the treble frequency . Due to this, in hybrid drivers, the use of balanced armature drivers together with dynamic drivers gives an improved and more balanced sound signature.
Which headphone driver do you prefer? Comment below.
If you have any questions on the six headphones drivers or more information, please comment below, and I will get back to you.